Bilateral Subacute/Chronic Endophthalmitis Leading to Complex Combined Retinal Detachment
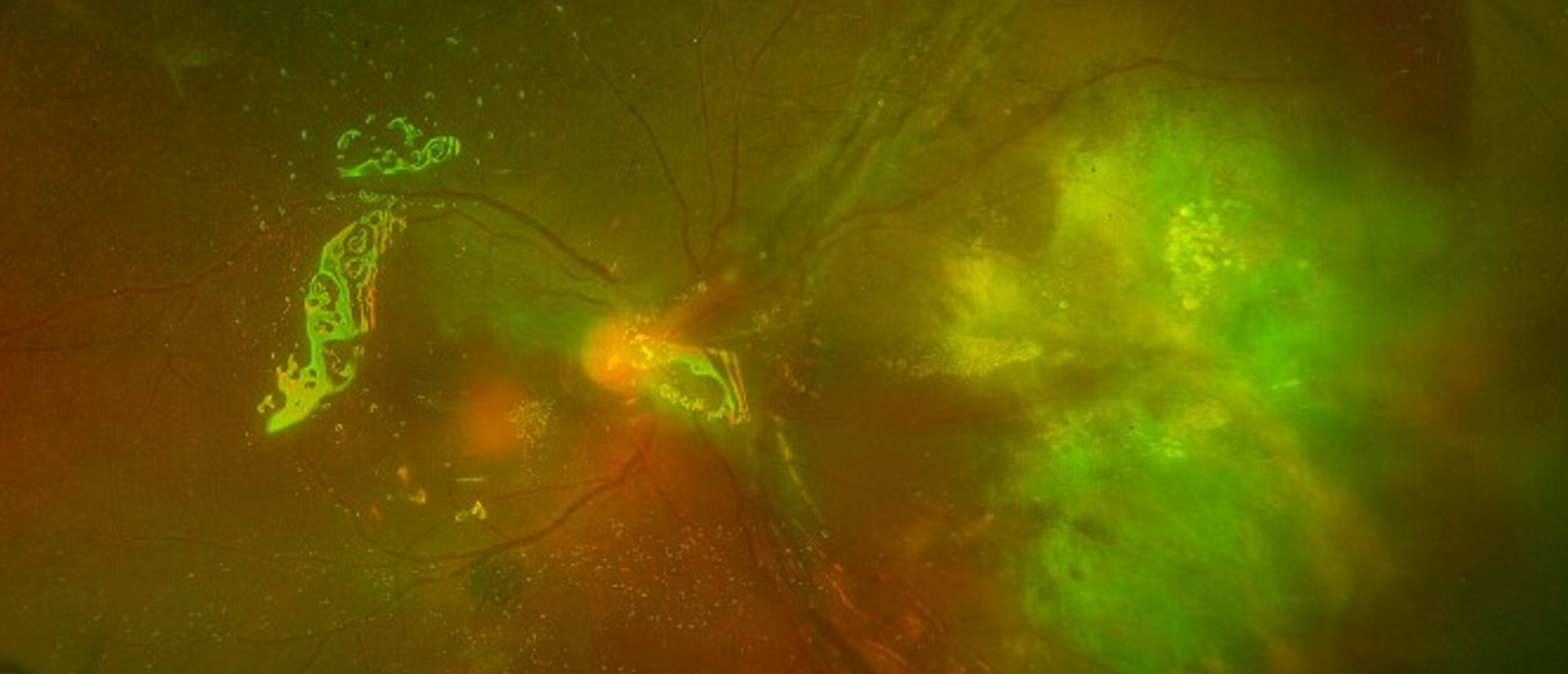
A patient with past medical history of chronic sciatica and recurrent skin abscesses presented to an outside hospital with positive blood, urine, and skin abscess cultures positive for methicillin sensitive staphylococcus aureus. He subsequently developed bilateral blurry vision in both eyes and was transferred to an affiliated tertiary care hospital for ophthalmologic evaluation. Examination while admitted was significant for hand motion vision in both eyes, posterior synechiae of the iris, and bilateral serous appearing retinal detachments with significant intraocular inflammation and possible subretinal abscesses. Further imaging demonstrated a rhegmatogenous component to the detachment along with a possible break on ultrasound. After discharge from the inpatient unit at the hospital, the patient underwent prompt bilateral pars plana vitrectomy with membrane peel and laser barricade of subretinal abscesses. On most recent follow-up, the patient’s best corrected visual acuity had improved to 20/300 OD and 20/60 OS.
Presentation Date: 05/13/2021
Issue Date: 05/21/2021
Please log in or click on ENROLL ME to access this course.